There are many ways to propagate plants. Each plant is propagated in a different way: by seeds, spores, shoots, leaves, division of the bush. Each of these methods requires attention and compliance with a certain sequence. Seed reproduction is the production of a new plant, the emergence of which is due to the pollination of two sex cells: male and female, resulting in the formation of a seed. With such reproduction, a new plant begins to develop with all the changes and transformations that occurred in previous plants. That is, we can get a plant that will differ in flower color and leaf shape from the parent plant.
Propagation by seeds allows you to get a large number of plants.
Basic rules of reproduction by seeds:
- The seed must be fresh (this affects how the seed will germinate).
- Carefully pack the unused seeds back in the package or in paper, protect the seeds from moisture.
- The germination time depends on the type of plant. To accelerate seed germination, soak the seeds in warm water for 1-2 days.
- Prepare the land (the land must be sterile and neutral).
- The vessel should be wide, but not deep, with a cover.
- Sow the seeds.
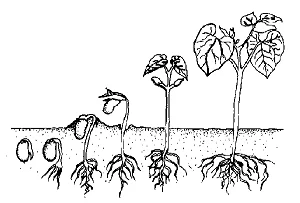
How to sow seeds?
Different methods are used:
- Very small seeds, such as those of petunia or lobelia, are mixed with sand before sowing in order to sow evenly on moistened soil. Such a tiny seed should not be sprinkled with earth.
- Small seeds are sown in shallow depressions made in the ground; before sowing, add water at room temperature. The distance between the depressions should be 3-4 cm.
- Medium and large seeds are sown in depressions of 1 – 3 cm. The seeds are placed at a distance of 2 – 5 cm from each other, sprinkled with earth to a depth twice the diameter of the seed. Cover with film, lid or glass.
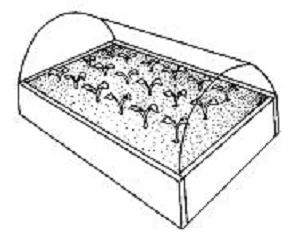
Next, we carefully monitor the soil moisture. In no case should the soil dry out. Seeds that are not sprinkled with earth and not covered with a film dry especially quickly at home.
In a mini-greenhouse, on the contrary, due to high humidity, it is easy to overmoisten the ground, and the ground will begin to be covered with white fungus. To avoid waterlogging of the soil, make several holes in the lid for air ventilation. The humidity of the substrate is checked daily. Soft water at room temperature is used for watering.
The time of emergence of seedlings depends on the size of the seed and the type of plant.
How to water seeds and seedlings?
After emergence, high humidity should be maintained. If the seed is too thick, it needs to be thinned. Young seedlings are very delicate, so it is especially important to follow the correct watering regime (humidity must be maintained evenly and constantly), you need to water them carefully so that the jets of water do not wash away the small seeds, you can use a sprayer, or pour water into a tray.
Air temperature in the greenhouse
It is equally important to observe the temperature regime. For subtropical species of plants, room temperature is enough, and for tropical species, it should be higher than 25-28 °.
It is wrong to think that the higher the temperature, the better it is for plants – not for everyone. It is more important to maintain its stability.
Young plants are pruned when they have four real leaves.
Reproduction by spores is characteristic of ferns and mushrooms
Their spores are sown in pre-hardened light, loose, moist peat substrate with sand. The mixture is poured onto a flat surface and covered from above with polyethylene film or glass, transferred to a shaded place until the sprouts appear. After the appearance of small green plates, the ground is watered from time to time, you can use a sprayer, or pour water into a tray. Drainage at the bottom is mandatory. The optimal temperature is 22 – 25 °.
Grown seedlings are transplanted into separate pots.

